Pancreatic Head Mass, How Can We Treat It?
Chronic Pancreatitis: Surgical Treatment
Massimo Falconi, Luca Casetti, Roberto Salvia, Nora Sartori, Rossella Bettini, Giuseppe Mascetta, Claudio Bassi, Paolo Pederzoli
Division of Endocrine Surgery, Department of Surgical and Gastroenterological Sciences. Verona, Italy











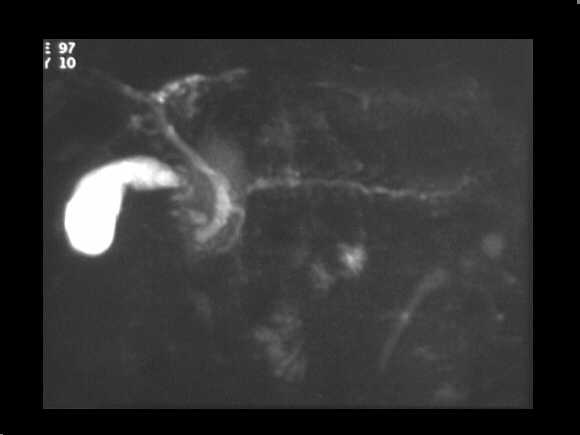
Obstructive chronic pancreatitis. MRCP examination demonstrates the chain of lakes pattern of the MPD. The CBD is also dilated.
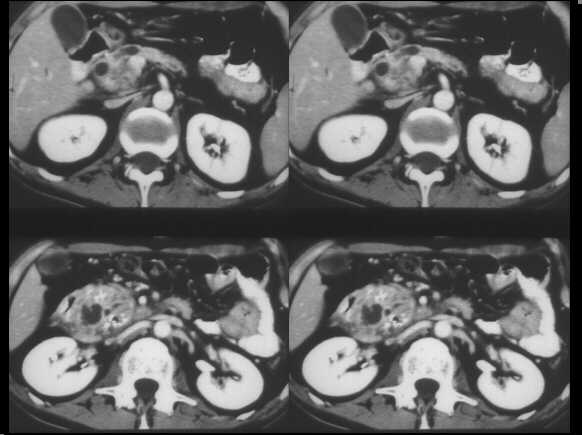
Mass-forming chronic pancreatitis. Spiral CT examination after c.m. administration. In the venous phase, the pancreatic head appears enlarged, slightly hypodense towards the remainder of the gland. A dilated MPD is recognizable within.



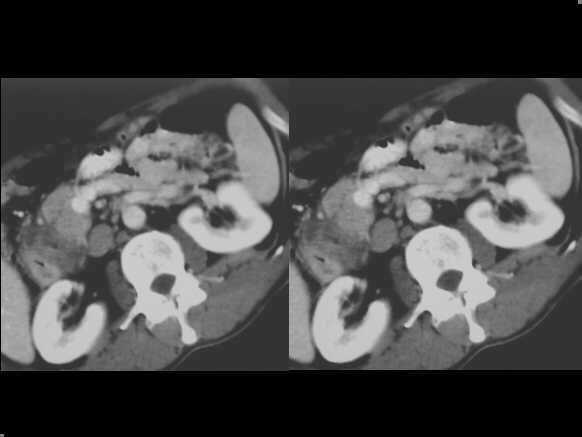
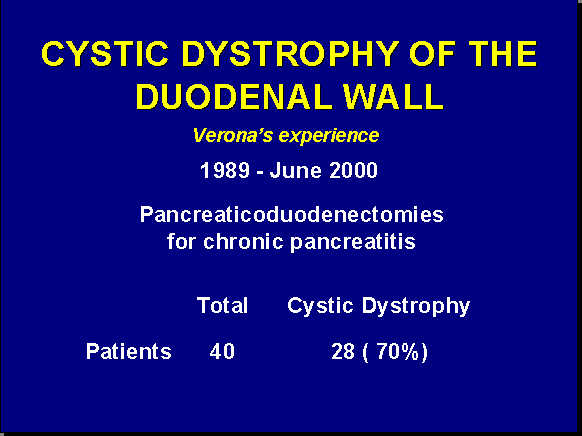
Cystic dystrophy of the duodenal wall – solid variant. Spiral CT examination in the venous contrastographic phase shows a thick, solid sheet-like mass between the duodenum and the pancreatic head. The fibrotic tissue is clearly hypodense in comparison to the pancreatic parenchyma.
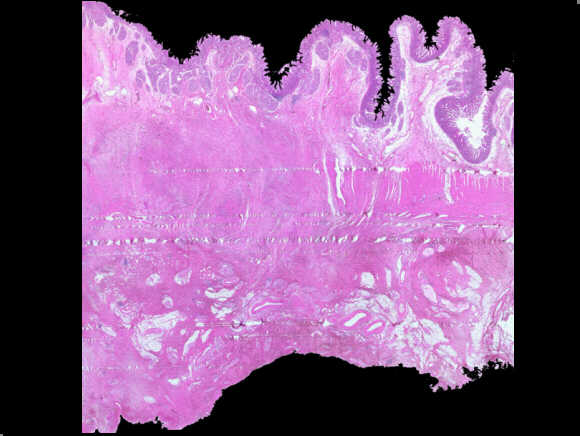
Duodenal wall in a “groove pancreatitis”. The histological important sign is the hypertrophy and the fibrosis of the muscolaris propria and the expansion of the “groove,” a virtual space, in the posterior face of the pancreata, between duodenum, pancreata and choledocus.
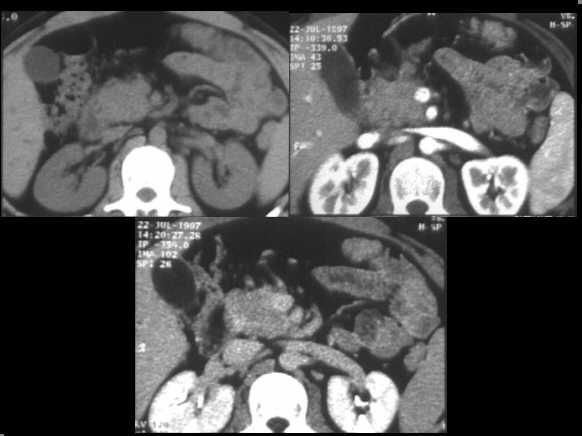
Focal autoimmune pancreatitis of the head. Spiral CT examination, before and after c.m. administration, demonstrates an enlarged head, which appears hypodense in the arterial contrastographic phase towards the spleen. Hypodensity remains appreciable in the venous phase.
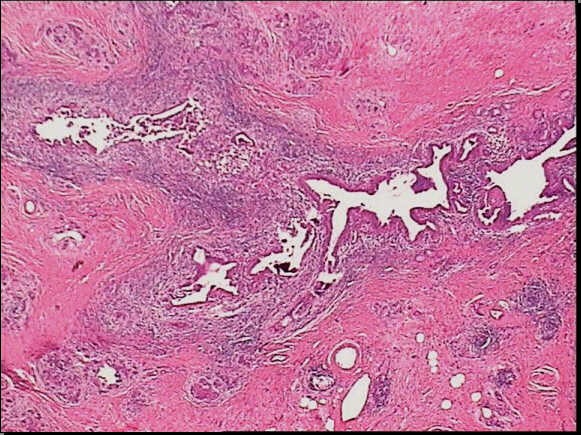
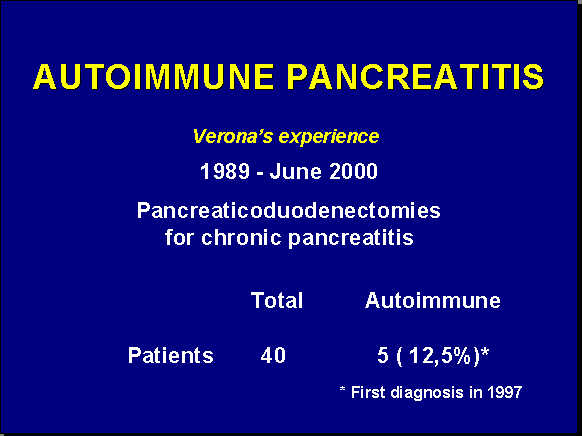
Low-power view of a autoimmune pancreatitis showing a periductular inflammatory cells. The remainder of pancreatic tissue is fibrotic with complete acinar atrophy.
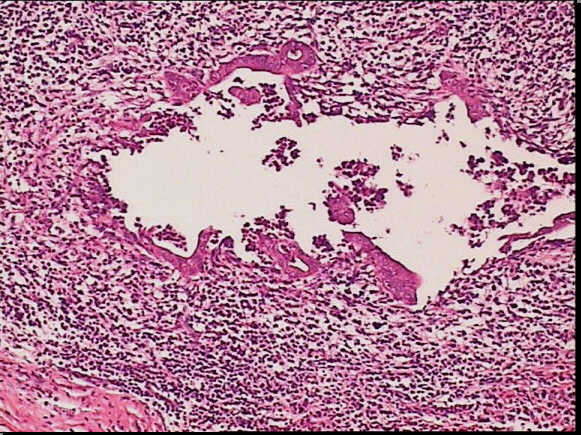
High-power view of the same slide shows the heavy inflammatory infiltrate in the epithelium layer with erosion and duct distorsion.
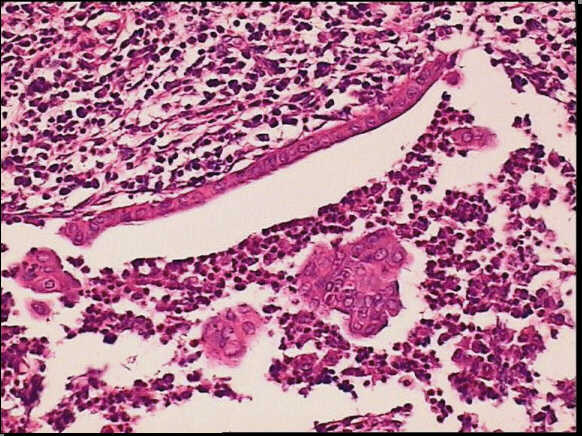
High-power view of the same slide shows the heavy inflammatory infiltrate in the epithelium layer with erosion and duct distorsion.

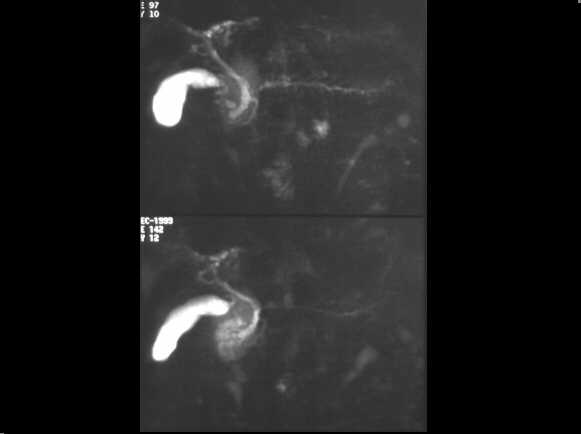
Chronic pancreatitis before sphynterotomy.
MRCP examination demonstrates the chain of lakes pattern of the MPD. The CBD is
also dilated.
Same case after sphynterotomy. The MPD appears normal.
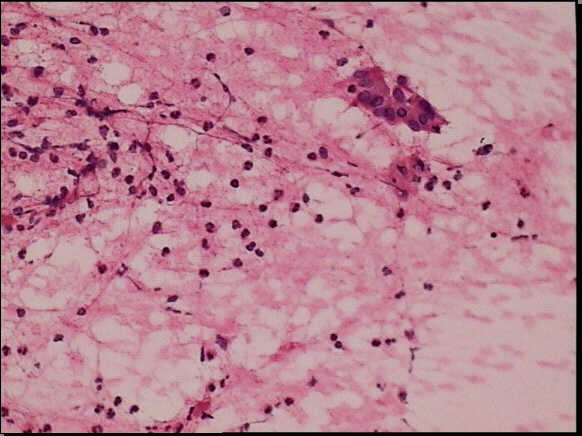
Fine needle aspiration of an autoimmune pancreatitis. In this aspirate, cohesive ductal cells and inflammatory cells can be observed.