Reactive Lymphoid Hyperplasia of the Pancreas: A Clinical Conundrum
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.6092/1590-8577/1327Keywords:
Pseudolymphoma, Pancreas, PancreatectomyAbstract
Context Localized reactive lymphoid hyperplasia is a rare condition characterized by the presence of lymphoid follicles. Case report We describe a case of a 60-year-old woman who presented with right upper quadrant pain and was found to have a reactive nodular hyperplasia of the pancreas involving the uncinate process, body and tail of the gland. Due to the multifocal distribution of these hypoechoic vascular lesions, a total pancreatectomy was performed since malignancy could not be safely excluded. Conclusion There have been a handful of cases reporting reactive lymphoid hyperplasia affecting the pancreas; however, it is uncommon to perform such a radical pancreatic resection for this benign condition.
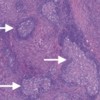
Image: Several hyperplastic lymphoid follicles.
Downloads
References
Amer A, Mafeld S, Saeed D, Al-Jundi W, Haugk B, et al. (2012) Reactive lymphoid hyperplasia of the liver and pancreas. A report of two cases and a comprehensive review of the literature. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol 36: e71-80.
Babaryka I, Thomas E (1981) [Pancreatitis lymphomatosa (author's transl)]. Zentralbl Allg Pathol 125: 315-318.
Hatzitheoklitos E, Buchler MW, Friess H, DiSebastiano P, Poch B, et al. (1994) Pseudolymphoma of the pancreas mimicking cancer. Pancreas 9: 668-670.
Kim JW, Shin SS, Heo SH, Jeong YY, Kang HK, et al. (2011) Imaging findings of localized lymphoid hyperplasia of the pancreas: a case report. Korean J Radiol 12: 510-514.
Nakashiro H, Tokunaga O, Watanabe T, Ishibashi K, Kuwaki T (1991) Localized lymphoid hyperplasia (pseudolymphoma) of the pancreas presenting with obstructive jaundice. Hum Pathol 22: 724-726.
Nakata B, Amano R, Matsuoka J, Sugimori S, Ohsawa M, et al. (2012) Spontaneously complete regression of pseudolymphoma of the remnant pancreas after pancreaticoduodenectomy. Pancreatology 12: 215-218.
Tokunaga O, Watanabe T, Morimatsu M (1987) Pseudolymphoma of the stomach. A clinicopathologic study of 15 cases. Cancer 59: 1320-1327.
Bergman R (2010) Pseudolymphoma and cutaneous lymphoma: facts and controversies. Clin Dermatol 28: 568-574.
Chang DW, Weiss PR (1995) Pseudolymphoma of the breast. Plast Reconstr Surg 95: 145-147.
Abbondanzo SL, Rush W, Bijwaard KE, Koss MN (2000) Nodular lymphoid hyperplasia of the lung: a clinicopathologic study of 14 cases. Am J Surg Pathol 24: 587-597.
Saltzstein SL (1963) Pulmonary Malignant Lymphomas and Pseudolymphomas: Classification, Therapy, and Prognosis. Cancer 16: 928-955.
Zen Y, Fujii T, Nakanuma Y (2010) Hepatic pseudolymphoma: a clinicopathological study of five cases and review of the literature. Mod Pathol 23: 244-250.
Knowles DM, Jakobiec FA, McNally L, Burke JS (1990) Lymphoid hyperplasia and malignant lymphoma occurring in the ocular adnexa (orbit, conjunctiva, and eyelids): a prospective multiparametric analysis of 108 cases during 1977 to 1987. Hum Pathol 21: 959-973.
Adsay NV, Basturk O, Klimstra DS, Kloppel G (2004) Pancreatic pseudotumors: non-neoplastic solid lesions of the pancreas that clinically mimic pancreas cancer. Semin Diagn Pathol 21: 260-267.
Ishida M, Nakahara T, Mochizuki Y, Tsujikawa T, Andoh A, et al. (2010) Hepatic reactive lymphoid hyperplasia in a patient with primary biliary cirrhosis. World J Hepatol 2: 387-391.
Choi TS, Doh KS, Kim SH, Jang MS, Suh KS, et al. (2003) Clinicopathological and genotypic aspects of anticonvulsant-induced pseudolymphoma syndrome. Br J Dermatol 148: 730-736.
Pham-Ledard A, Vergier B, Doutre MS, Beylot-Barry M (2010) Disseminated cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia of 12 years' duration triggered by vaccination. Dermatology 220: 176-179.
Miyoshi S, Hamada H, Katayama H, Hamaguchi N, Irifune K, et al. (2010) A case of pulmonary nodular lymphoid hyperplasia with a resected cavity, followed by spontaneous regression of the remaining lesions. Intern Med 49: 1617-1621.
Kulow BF, Cualing H, Steele P, VanHorn J, Breneman JC, et al. (2002) Progression of cutaneous B-cell pseudolymphoma to cutaneous B-cell lymphoma. J Cutan Med Surg 6: 519-528.
Schwartz MS, Sherman H, Smith T, Janis R (1989) Gastric pseudolymphoma and its relationship to malignant gastric lymphoma. Am J Gastroenterol 84: 1555-1559.
Machida T, Takahashi T, Itoh T, Hirayama M, Morita T, et al. (2007) Reactive lymphoid hyperplasia of the liver: a case report and review of literature. World J Gastroenterol 13: 5403-5407.
Saif MW (2006) Primary pancreatic lymphomas. JOP 7: 262-273.
Cortelazzo S, Ponzoni M, Ferreri AJM, Dreyling M (2012) Mantle cell lymphoma. Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology 82: 78-101.
Witzig TE, Geyer SM, Ghobrial I, Inwards DJ, Fonseca R, et al. (2005) Phase II Trial of Single-Agent Temsirolimus (CCI-779) for Relapsed Mantle Cell Lymphoma. Journal of Clinical Oncology 23: 5347-5356.
Stanford (2012) Surgical Pathology Criteria - Lymphomas. Stanford School of Medicine.
http://surgpathcriteria.stanford.edu/bcell/mantle/differentialdiagnosis.html#t1
Suzuki H, Saito Y, Hibi T (2009) Helicobacter pylori and Gastric Mucosa-associated Lymphoid Tissue (MALT) Lymphoma: Updated Review of Clinical Outcomes and the Molecular Pathogenesis. Gut Liver 3: 81-87.
Husson H, Carideo EG, Neuberg D, Schultze J, Munoz O, et al. (2002) Gene expression profiling of follicular lymphoma and normal germinal center B cells using cDNA arrays. Blood 99: 282-289.
Klapper W (2011) Pathobiology and diagnosis of follicular lymphoma. Semin Diagn Pathol 28: 146-160.