Effect of Protein Kinase C on Glucose-Mediated Insulin Secretion in HIT-T15 Cells
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.6092/1590-8577/372Keywords:
Potassium Channels, Protein Kinase C, StaurosporineAbstract
Objective To clarify the regulation of protein kinase C on glucose-mediated insulin secretion. Main outcome measures We examined the effect of protein kinase C on the cytosolic free Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i) and the activity of Ca2+-activated K+ channels (KCa-channel) in the insulinoma cell line, HIT-T15. Results Glucose at a concentration of 10 mmol/L increased the secretion of insulin. This increase was partly inhibited by 1 nmol/L staurosporine, a protein kinase C inhibitor. Staurosporine (1 nmol/L) also attenuated the glucose-induced elevations in [Ca2+]i. On the contrary, glibenclamide (100 nmol/L) specifically blocked ATP-sensitive K+ channels, and increased both [Ca2+]i and insulin secretion, but staurosporine had no effect on them. Patch clamp studies showed that 10 mmol/L glucose almost completely blocked KCa channel activity, an effect that was reversed by 1 nmol/L staurosporine. Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (1 mmol/L), a protein kinase C activator, also decreased KCa channel activity. Conclusions These results indicate that the activation of protein kinase C is involved in the glucose-induced release of insulin by modulating K+ channel function in HIT-T15 cells.
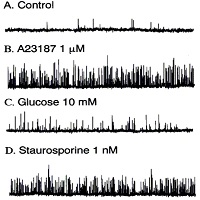
Image: Inhibitory effects of glucose on KCa channels.
Downloads
References
Ashcroft FM, Harrison DE, Ashcroft SJH. Glucose induces closure of single potassium channels in isolated rat pancreatic beta-cells. Nature 1984; 312:446-8.
Cook DL, Hales CN. Intracellular ATP directly blocks K+ channels in pancreatic B-cells. Nature 1984; 311:271-3.
Rorsman P, Trube G. Glucose dependent K+-channels in pancreatic beta-cells are regulated by intracellular ATP. Pflugers Arch 1985; 405:305-9.
Arkhammar P, Nilsson T, Rorsman P, Berggren PO. Inhibition of ATP-regulated K+ channels precedes depolarization-induced increase in cytoplasmic free Ca2+ concentration in pancreatic beta-cells. J Biol Chem 1987; 262:5448-54.
Schmid-Antomarchi HS, Weille JD, Fosset M, Lazdunski M. The receptor for antidiabetic sulfonylureas controls the activity of the ATP-modulated K+ channel in insulin-secreting cells. J Biol Chem 1987; 262:15840-4.
Henquin JC, Charles S, Nenquin M, Mathot F, Tamagawa T. Diazoxide and D 600 inhibition of insulin release. Diabetes 1982; 31:776-83.
Gembal M, Gilon P, Henquin JC. Evidence that glucose can control insulin release independently from its action on ATP-sensitive K+ channels in mouse B cells. J Clin Invest 1992; 89:1288-95.
Gembal M, Detimary P, Gilon P, Gao ZY, Henquin JC. Mechanisms by which glucose can control insulin release independently from its action on adenosine triphosphate-sensitive K+ channels in mouse B cells. J Clin Invest 1993; 91:871-80.
Aizawa T, Sato Y, Ishihara F, Taguchi N, Komatsu M, Suzuki N, et al. ATP-sensitive K+ channel-independent glucose action in rat pancreatic b-cell. Am J Physiol 1994; 266:C622-7.
Berridge MJ, Irvine RF. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature 1984; 312:315-21.
Streb H, Irvine RF, Berridge MJ, Schulz I. Release of Ca2+ from a nonmitochondrial intracellular store in pancreatic acinar cells by inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate. Nature 1983; 306:67-9.
Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumor promotion. Nature 1984; 308:693-8.
Tanigawa K, Kuzuya H, Imura H, Taniguchi H, Baba S, Takai Y, et al. Calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase in rat pancreas islets of langerhans. FEBS Lett 1982; 138:183-6.
Thams P, Capito K, Hedeskov CJ. Endogenous substrate proteins for Ca2+-calmodulin-dependent, Ca2+-phospholipid-dependent and cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinases in mouse pancreatic islets. Biochem J 1984; 221:247-53.
Lord JM, Ashcroft SJH. Identification and characterization of Ca2+-phospholipid-dependent protein kinase in rat islets and hamster beta-cells. Biochem J 1984; 219:547-51.
Hutton JC, Peshavaria M, Brocklehurst KW. Phorbol ester stimulation of insulin release and secretory-granule protein phosphorylation in a transplantable rat insulinoma. Biochem J 1984; 224:483-90.
Deeney JT, Cunningham BA, Chheda S, Bokvist K, Juntti-Berggren L, Lam K, et al. Reversible Ca2+-dependent translocation of protein kinase C and glucose-induced insulin release. J Biol Chem. 1996; 271:18154-60.
Nishizuka Y. Studies and perspectives of protein kinase C. Science 1986; 233:305-12.
Higashida H, Brown DA. Two polyphoshatidylinositide metabolites control two K+ currents in a neuronal cell. Nature 1986; 323:333-5.
Findlay I, Dunne MJ, Petersen OH. ATP-sensitive inward rectifier and voltage- and calcium-activated K+ channels in cultured pancreatic islet cells. J Membr Biol 1985; 88:165-72.
Hamill OP, Marty A, Neher E, Sakmann B, Sigworth FJ. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch 1981; 391:85-100.
Nishizuka Y. The family of protein kinase C for signal transduction. J Am Med Assoc 1989; 262:1826-33.
Malaisse WJ, Sener A, Herchuelz A, Carpinelli AR, Poloczek P, Winand J, et al. Insulinotropic effect of the tumor promoter 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate in rat pancreatic islets. Cancer Res 1980; 40:3827-31.
Malaisse WJ, Lebrun P, Herchuelz A, Sener A, Malaisselagae F. Synergistic effect of a tumor-promoting phorbol ester and a hypoglycemic sulfonylurea upon insulin release. Endocrinology 1983; 113:1870-7.
Hii CST, Jones PM, Persaud SJ, Howell SL. A re-assessment of the role of protein kinase C in glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. Biochem J 1987; 246:489-93.
Hughes SJ, Chalk JG, Ashcroft SJH. The role of cytosolic free Ca2+ and protein kinase C in acetylcholine-induced insulin release in the clonal beta-cell line, HIT-T15. Biochem J 1990; 267:227-32.
Wollheim CB, Dunne MJ, Peter-Riesch B, Bruzzone R, Pozzan T, Petersen OH. Activators of protein kinase C depolarize insulin-secreting cells by closing K+ channels. EMBO J 1988; 7:2443-9.
Eddlestone GT, Ribalet B, Ciani S. Comparative study of K channel behavior in beta cell lines with different secretory responses to glucose. J Membr Biol 1989; 109:123-34.